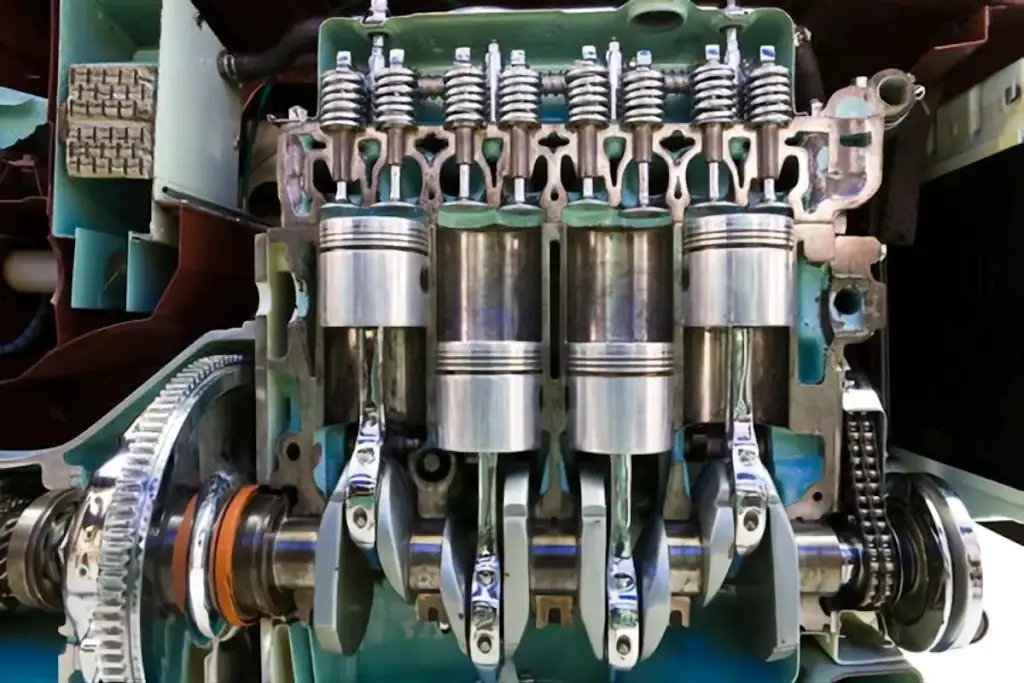
In 1876 the first commercially successful internal combustion engine was introduced to the world; this was the base of the automotive revolution. Nowadays, When looking around in the street and seeing all these automotive vehicles moving in the streets outside, I can’t imagine what our lives would look like if there weren’t combustion engines in the world.
Who invented the first internal combustion engine?
If you searched on google for the inventor of the first internal combustion engine, you might find many claim Nikolaus otto, but that is not true; Otto is known for inventing the Modern combustion engine, but the first commercially successful engine was invented by the Belgian inventor Étienne Lenoir in 1860.
Prior design (De Rivaz engine) was patented in 1807, but it wasn’t commercially successful. A first for the internal combustion engine, Lenoir’s engine was commercialized in enough quantities to be considered successful.
Lenoir engine story
Steam was used to power machinery at the time. Lenoir wanted compact engines that could run on coal gas as well as city or light gas, both of which were readily available in Paris. The idea was based on a steam engine that sucked in a mixture of 6% city gas and 94% air during the first half of the first stroke.
The uncompressed mixture was ignited halfway through the first stroke with a spark plug – another patented Lenoir invention. The expanding gas combination pushed the piston out with enormous force. The burnt gas mixture was ejected on the second stroke.
The engine only had one cylinder at the time, giving it a tendency to overheat. However, it was able to propel a three-wheeled vehicle that could travel approximately two miles per hour.
Lenoir’s machine combines numerous technologies of his period, including the steam engine, the newly invented Ruhmkorff ignition coil, and Lenoir’s patented spark plug. The first internal combustion engine having a double-sided operation, two-stroke action, and no preceding compression was invented.
What did Nikolaus Otto invent ?
Soon after, Nikolaus August Otto (1832–1891), a German engineer, invented an engine similar to Lenoir’s. It was called the atmospheric gas engine or the Flugkolben engine. This engine was a prototype for the ultimate four-stroke engine. This engine was already improving and causing a stir at that year’s World’s Fair in Paris.
In 1876, the ultimate breakthrough occurred. Otto created the four-stroke engine that year, later serving as a prototype for succeeding combustion engines. Because the fuel mixture is suitably renewed, four-stroke is more fuel-efficient. It was dubbed the Otto engine.
The invention of the diesel engine.
In 1878 Rudolph Diesel, a German inventor aimed to develop a more efficient engine, and in 1892 the diesel engine was born. It required many more years to build a cleaner and quieter diesel engine, which was more efficient than a regular internal combustion engine. Early diesel engines emitted sooty smoke and were initially employed mainly in trucks. New developments have improved the diesel engine in this form of the internal combustion. The conversion of fuel to energy differs between gasoline and diesel engines.
Diesel Vs. Gasoline engines
ICE can be powered by gas fuel such as natural gas, biogas and Liquid fuel such as heavy oil, crude oil, kerosene, renewable fuels, etc
Diesel and gasoline are the most commonly known fuel used by internal combustion engines, but what are the key differences between these two types? Let’s find out
Both types of engines consume fuel and convert it to energy through combustion (explosions). The main difference between the Diesel and the gasoline engines is how the explosions occur.
In a gasoline engine, fuel is combined with air, compressed by pistons, and ignited by spark plug sparks. However, with a diesel engine, the air is compressed first, followed by the fuel injection. When air is compressed, it heats up and ignites the fuel.
What is the difference between internal (ICE) and external combustion engines (EC)?
Internal combustion engines Are engines in which the combustion of fuel occurs solely in the cylinder, and the work on the piston is done by the burned gases or combustion products, which are then released through exhaust valves. This is the foundation of current CI and petrol engines.
On the other hand, External combustion Combustion occurs outside the piston cylinder, and the burnt gases are required to heat a secondary working fluid, like water, to generate steam, which is then used as the working fluid in the cylinders. The automobile is driven by force exerted by steam on the pistons.
Two-stroke vs four-stroke engine
To understand the differences between these two engines, you must first learn the fundamentals.
The piston goes up and down inside the cylinder throughout the combustion cycle of an engine. The terms “top dead center” and “bottom dead center” ) are used to describe the location of the piston within the cylinder. The position closest to the valves is TDC, and the position farthest from them is BDC. The piston goes from TDC to BDC or vice versa throughout a stroke. The full process of gas and air being injected into the piston, igniting it, and blowing the exhaust is known as a combustion revolution or combustion cycle:
Intake: As the piston descends the cylinder, a mixture of fuel and air is injected into the combustion chamber.
Compression occurs when the piston returns to the top of the cylinder and the intake valve are closed, compressing the gasses within.
Combustion: The air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark from the spark plug. which forces the piston to move downward
Exhaust: The piston moves upward in the cylinder to its original position, and the exhaust valve is opened.
The difference between a 4-stroke and 2-stroke engine is the number of times the piston goes up and down during each combustion cycle.
4-stroke: During each revolution of a 4-stroke engine, the piston completes two strokes: one compression stroke and one exhaust stroke, followed by a return stroke. The spark plugs only fire once every other revolution, and power is generated per four piston strokes. These engines also do not require pre-mixing of fuel and oil because the oil is contained in a separate compartment.
2-stroke: The combustion cycle in a 2-stroke engine is accomplished with just one piston stroke: a compression stroke followed by the explosion of compressed fuel. During the second stroke, the exhaust is let out, and a new fuel mixture is injected into the cylinder. The spark plugs ignite once every revolution, and power is generated every two piston strokes. Oil must also be pre-mixed with the fuel in two-stroke engines.
Types of internal combustion engines (layouts)
The engine is the vehicle’s brain. It has all of the power required to keep your car running. And your car would be nothing without it. However, there are numerous car engine types on the road.
Engines come in two different major designs. piston engines and rotary engines, piston engines come in different shapes and numbers of the piston, while rotary engines have only one layout
Inline engine
Inline engines are the most common type of engines; they are used in the vast majority of vehicles on the street, including heavy machines and ships. It has all of its cylinders lined up and facing upward. The 4-cylinder inline engine is the most common type of engine used in cars today; therefore, it’s likely that your car is equipped with one.
It’s smaller, lighter, and has fewer moving components than other engines. It rarely exceeds 2.5 to 3.0 liters on the downhill. The most common type of this layout in inline 4 and inline 6
Vee engine
From the front, this sort of engine appears to be shaped like the letter “V.” At their base, all cylinders face outwards and drive one common crankshaft.
However, this type of engine will not be found in a budget. The Vee engine is exclusively found in high-performance sports automobiles and SUVs. This is due to the Vee engine’s ability to fit more cylinders into a smaller space than other engine types. The most common type of Vee engines is the V6 and V8 engines.
VR and W engines,
This engine is very similar to the Vee engine, with a few exceptions. The VR and W engines, developed by Volkswagen, have cylinders with tiny spacing between them. Today, cars like the Bentley Mulsanne use this engine. The most common type of Vr engine is the Vr6, known for powering Volkswagon cars and the W16, which powers Bugatti cars.
Flat engine
The flat engine, also known as the boxer engine, is one-of-a-kind. It consists of two banks of two cylinders lying flat on their sides. These cylinders point away from one another, keeping gravity low and improving handling. The Japanese automaker Subaru is known for its boxer engines used by almost all its vehicles, and it can be found in luxury vehicles such as Porsche.
Rotary engine (Wankel engine)
The German engineer Felix Wankel is the inventor of the Wankel engines that was named after him. Instead of pistons, the Rotary engine uses rotors. It has a small design with a curved, rectangular shape. A single-direction center rotor creates intake, compression, power, and exhaust while the engine is running. Because of its design, this engine has a low torque output and is only found in Mazda RX vehicles.
The automotive revolution: Karl Benz and the invention of the car
In 1879 Karl Benz was granted a patent for his internal combustion engine, a reliable two-stroke gas engine based on the design of Nikolaus Otto’s four-stroke engine. Later, Benz invented and constructed his four-stroke engine for use in his vehicles, which were the first mass-produced autos.
In 1886, Karl Benz patented the three-wheeled Motor Car, often known as the “Motorwagen.” It was the first true, modern automobile; hence Benz is commonly credited as the inventor of the automobile. Benz also developed his throttle system, spark plugs, gear shifters, water radiator, carburetor, and other automobile components. Benz subsequently established a car firm that still exists today as the Daimler Group.
At this moment it was obvious that all of these german are reshaping with their inventions the world and the human lifestyle for the next 200 years
The impact of ICE engines on humanity
More than 250 million vehicles in the United States and 1.2 billion worldwide rely on internal combustion engines, which provide excellent drivability and durability. They can use renewable or alternative fuels in addition to gasoline or Diesel (e.g., natural gas, propane, biodiesel, or ethanol). They can also be used with hybrid-electric powertrains to improve fuel economy or plug-in hybrid electric systems to boost hybrid electric vehicle range.
Conclusion
Many inventors contributed to the invention of the internal combustion engine until it reached its current design, but the most significant ones are Étienne Lenoir( 1822-1900), Nikolaus Otto (1832-1891) and Rudolf Diesel (1858-1913). When the first commercially successful engine was debuted in the 1860s by Lenoir, it had a greater impact on the economy, ecology, and daily lives of millions of people than any other technology in the twentieth century. Otto’s engines utilized spark plugs for fuel combustion, while Diesel’s engines accomplished this through high compression.
These technologies made it possible to power automobiles, locomotives, ships, and aeroplanes, paving the way for widespread mobility and the escalating global flow of products. Concurrently, this has resulted in huge changes to the terrain and environment due to the construction of innumerable roads, worldwide air pollution, and the rising resource and energy consumption of high-energy societies.