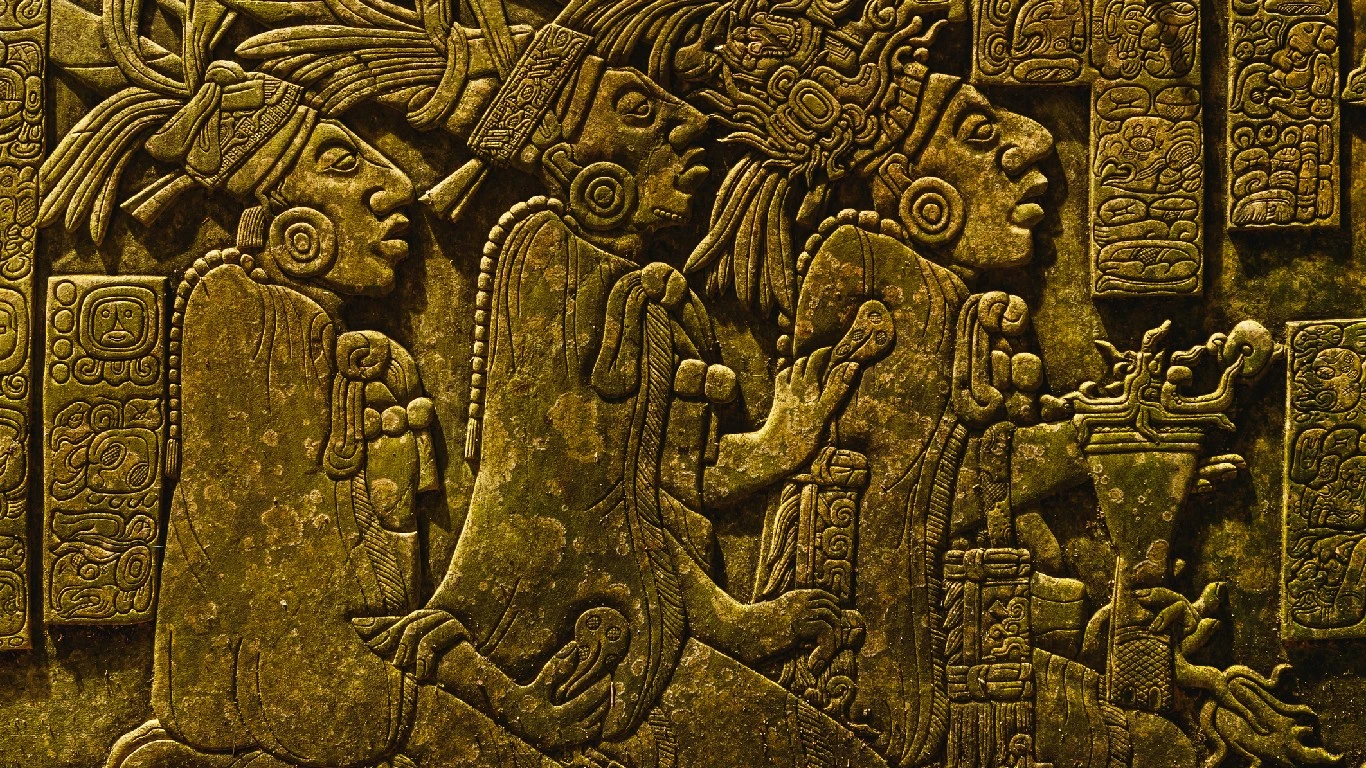
A Group of researchers from different universities in America and Guatemala found a huge 2000-year-old Mayan civilization present in Guatemala. The group of researchers used LIDAR for the discovery.
Why LiDAR?
LIDAR is a sensing device used to check the crust of the earth. It uses laser light instead of radio waves for detection purposes, which is much more common than radar. A Group of researchers used lidar because it penetrates jungles and finds what is beneath them.
Massive Maya civilization was found while mapping Guatemala
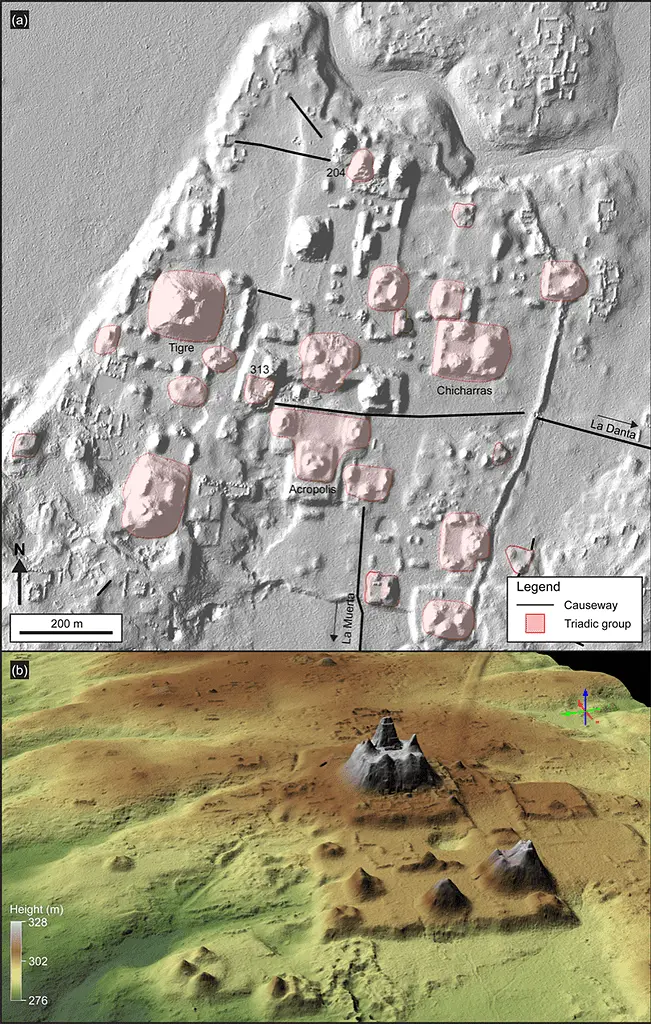
According to a news release, while mapping a region of Guatemala, the researchers discovered what they called a large ancient Mayan civilization.
According to their maps, the prehistoric civilization comprised more than 1,000 sites, most of which were linked by numerous causeways and covered a space of around 650 square miles.
According to theories, early Mesoamerican deals that were rarely
populated are refuted by the reality that the inhabitants of the settlements had earlier been packed tight together.
The 110 miles of movable wooden bridges made it quite simple for the civilization’s inhabitants to reach the adjacent communities (cleared, raised beds used as highways). The researchers highlight the possibility for measures at group projects that the transportation infrastructure affords.
Based on the findings of massive platforms and pyramids in several villages, experts hypothesize that some settlements may have served as concentrated hubs for politics, work, and entertainment.
They further claim that a prior study discovered that some communities had ball courts for various neighborhood games. The researchers also discovered that the civilization’s inhabitants had constructed reservoirs and canals to transport and store water during dry seasons.
Pyramids and E-Terrain in architecture
The Recent discoveries also showed that the kingdom contained elaborate architectural buildings.
E-groups, used for rites and ceremonies, comprise several buildings, usually a pyramid facing a platform flanked by a bigger plaza. According to the researchers, these groups were discovered in several communities around the kingdom, and their sizes varied according to the complexity of the settlement.
According to researchers, fewer than one E group lived in several tiny villages.

Additionally, settlements had triadic structures, usually pyramids.
According to the researchers, the intricate designs and materials utilized to make these pyramids show organization inside ancient settlements.
According to the experts:
“The entire building may have had 6,000,000 to 10,000,000 person-days of work.”
A fugitive buried a box of coins in a cave near Israel two thousand years ago. It was just discovered.
For 2,500 years, no one could explain this riddle, but one college student had a “eureka moment.”
Roman emperors once had a mansion with a 2,000-year-old mosaic floor.
In the north of Guatemala, a 2,000-year-old Mayan civilization was found.
Dams and reservoirs for controlling water
Researchers now better understand how much ancient civilizations managed their water supply because of the recent discovery.
According to scholars, civilizations in the Mirador-Calakmul Karst Basin relied on the nearby marshes as their water supplies, necessitating reservoirs to store water. The LiDAR data showed “a handful of massive reservoir systems designed to capture and control large volumes of water,” in addition to 195 artificial reservoirs.
The kingdom has also seen the discovery of several dams.
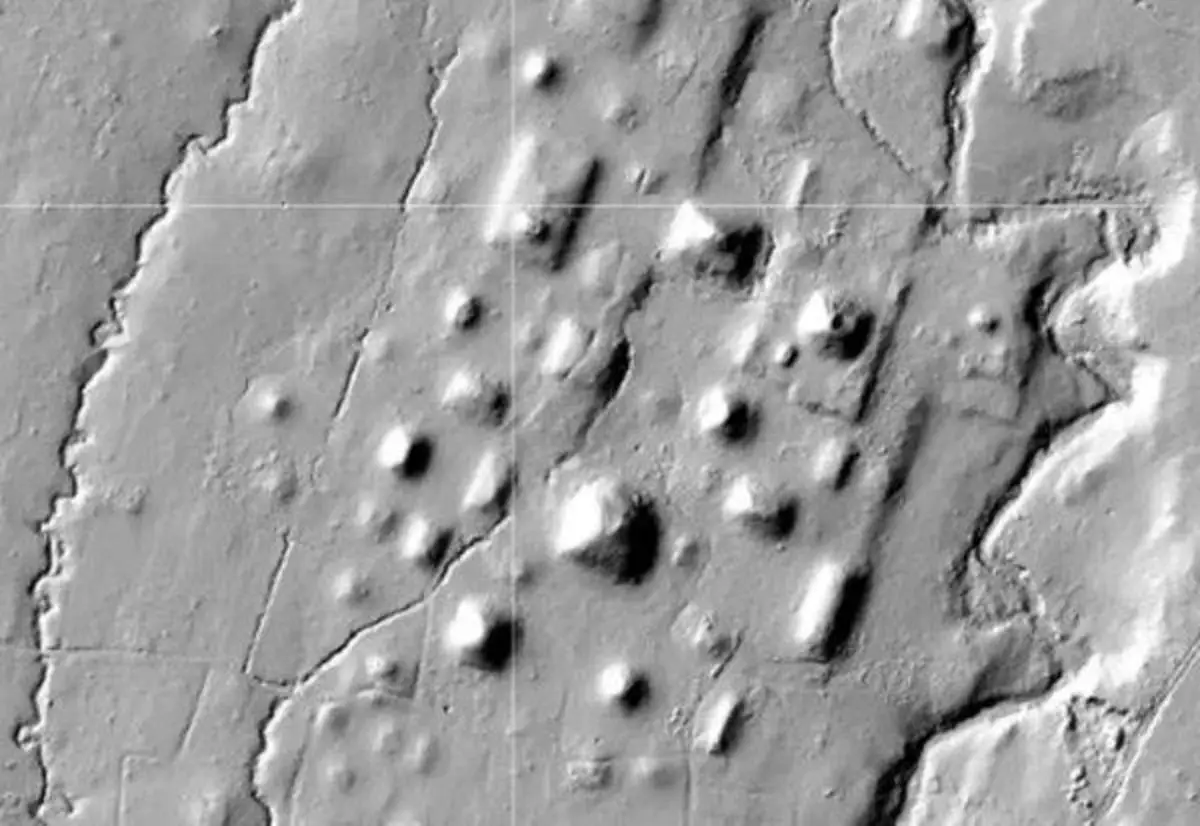

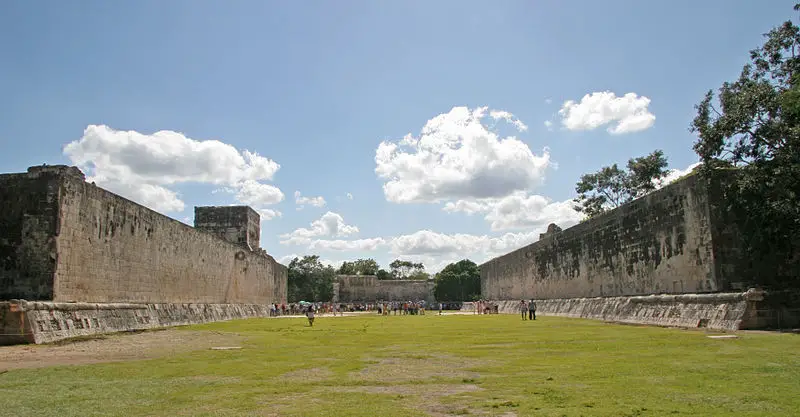
Mayan Ballcourts where also found
In the settlement network, archaeologists found a total of 30 ball courts, according to the report.
The courtyards, which ranged in length from 30 to 65 feet, sometimes had “two parallel constructions, commonly in a north-south axis,” according to the researchers.
Three tiny and four big courtyards have been found at El Mirador, one of the major sites. The largest courts are found in the Great Central Acropolis of the site, indicating where the ruler’s possible seat of power was.
Causeways for traveling to other communities
It was reasonably easy for civilization’s citizens to move to their nearby villages or town, with great pleasure to the 110 miles of navigable causeways (also utilized as highways and raised beds). The researcher focused more on some important groups of people that the transportation infrastructure presents.
Some settlements may have operated as concentrated hubs for politics, work, and entertainment based on the discovery of large platforms and pyramids in some societies. A researcher also highlighted that a previous study found that few villages included ball courts used for various provincial games.
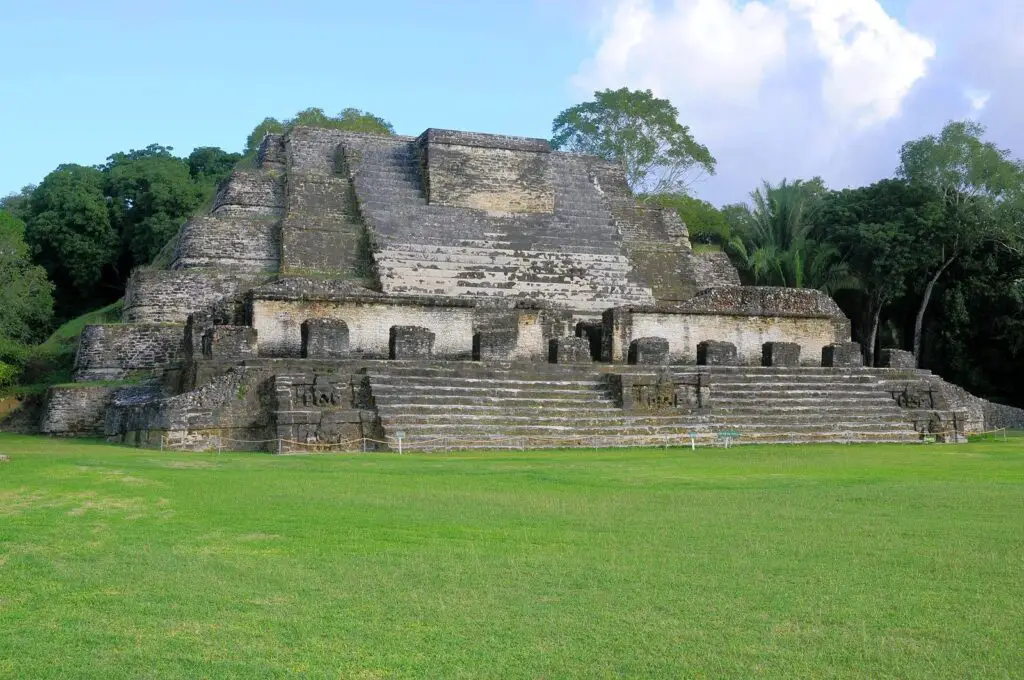

Civilized people of that also built reservoirs for moving from one place to another(transportation means), built canals, and stored water during dry seasons.
The “crowning brilliance” of causeways
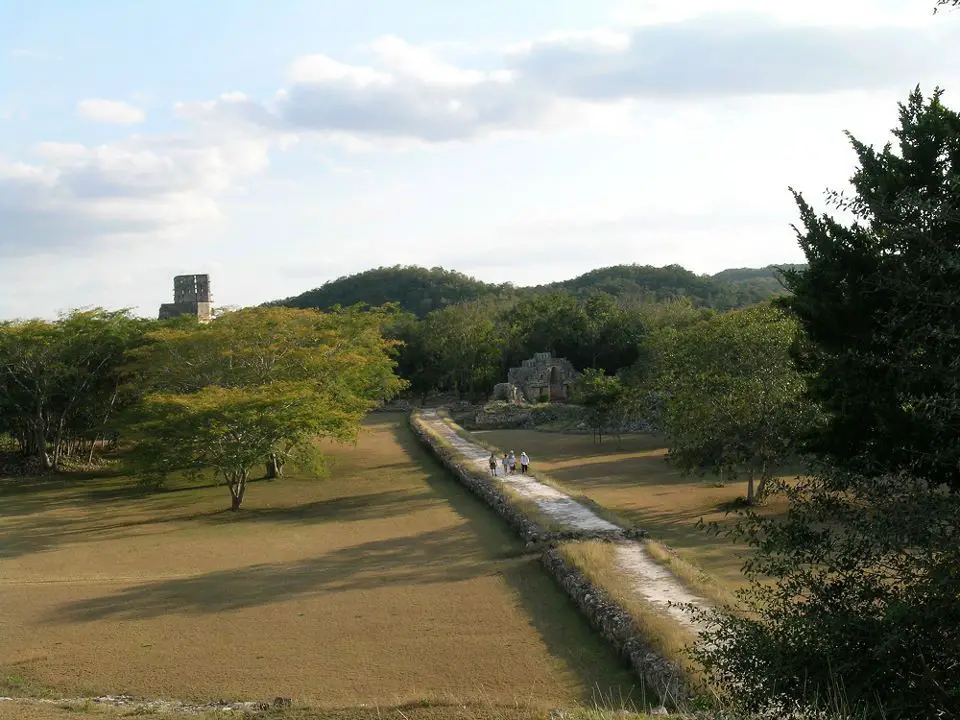

The Maya kingdom’s “crowning glory,” a branching network of causeways connected and connected places, suggested “intra-community connectedness and integration,” according to scholars.
Most of the system’s causeways were constructed using lime and clay mixtures, which involved a lot of labor.
According to research, a network of causeways connected the kingdom’s numerous villages.
According to the latest analysis, most of the dams were concentrated in El Mirador, the greatest civilization in the kingdom, indicating “an administrative centralization.” The system also emphasizes how political and economic institutions have evolved as a result of an authority
Details on the Maya Civilization
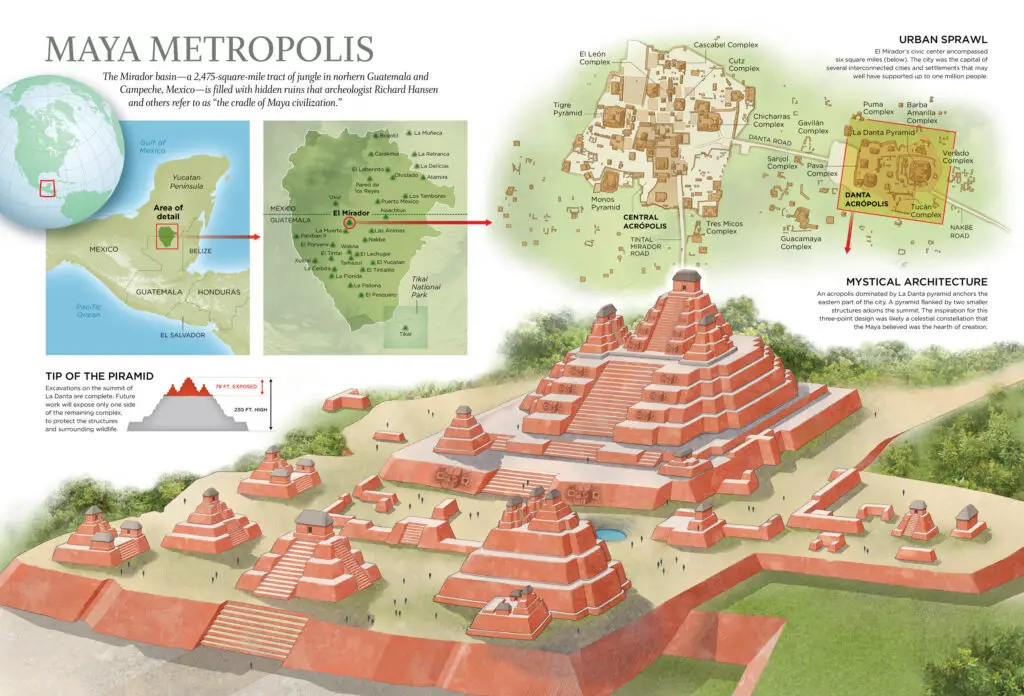
It was around 1500 BCE that the Mayans began settling down in towns and cultivating crops, according to Britannica. The Classic Period of Maya history occurred from roughly 250 to 900 CE. At its height, the Mayan civilization had more than 40 cities, each with a population of 5,000 and 50,000.
After the decline of the great cities of lowland Guatemala during the Post-Classic Era, the Yucatán Peninsula became a thriving metropolis for centuries (900–1519).
The Mayans controlled a huge swath of the northwest of Central America, including the modern-day countries of Guatemala, Honduras, Belize, El Salvador, and Nicaragua, as well as the ancient Mexican states of Chiapas and Yucatán. Even today, the Maya still reside in the same area.
At the turn of the century, more than five million people, the vast majority of whom also learned Spanish, spoke one of the roughly 30 Mayan languages.

Conclusion
A Group of researchers found a 2,000-year-old Mayan civilization in Guatemala using lidar technology. LIDAR is a sensing device that checks the earth’s crust with laser light instead of radio waves. According to their maps, the prehistoric civilization comprised more than 1,000 sites, most of which were linked by causeways and covered a space of around 650 square miles.
The LiDAR data showed “massive reservoir systems designed to capture and control large volumes of water,” as well as 195 artificial reservoirs. The kingdom has also discovered several dams, which scientists believe are crucial for managing the water supply.
Archaeologists have discovered courts, causeways, and canals from the Mayan civilization used to transport and store water during dry seasons. The largest courts are found in the Great Central Acropolis of El Mirador, indicating where the ruler’s possible seat of power was.
Some settlements may have operated as concentrated hubs for politics, work, and entertainment based on large platforms and pyramids.






