Have you noticed many design features and technologies that make windows more energy efficient and improve their durability, aesthetics, and functionality?
In buildings, it might help save energy. Additionally, windows play a crucial role in building envelopes and have a big impact on the overall energy budget. To keep buildings cooler, a group of researchers has discovered a way to make a novel hydrogel glass window.
A new way called novel hydrogen glass!
Have you ever noticed how hot a room or house feels when you enter it? This makes the scene inside the house uncomfortable and heated. Therefore, in addition to fans and AC, a cooling system is needed to maintain a comfortable environment in the space.
Here’s where cutting-edge hydrogel glass windows come into play.
What is Novel Hydrogel?
Novel hydrogels consist of novel formulations, including nanoparticles, nanoemulsions, microemulsions, liposomes, self-nano emulsifying drug delivery systems, cubosomes, etc.
Cross-linking of hydrophilic polymer chains in an aqueous environment results in the formation of hydrogels. They could be used for window engineering because of their water-rich and translucent properties.
They are used for different applications, from material use to pharmaceuticals.
In the past decade, there has been a rise in research on new hydrogels. There is a considerable probability that natural and synthetic polymer-based hydrogels will soon enter clinical trials and the market.
New hydrogel glass could save a lot of energy.
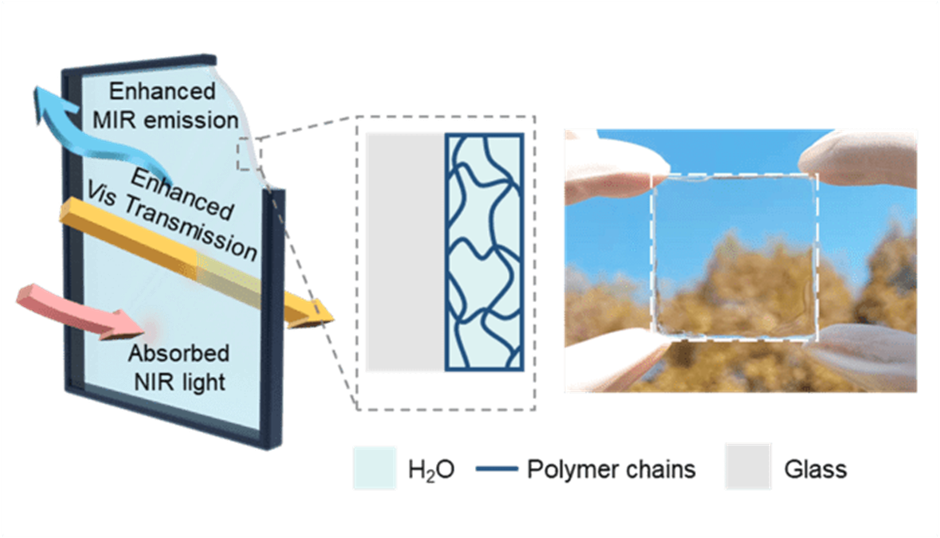
Apart from its wide range of applications, it is also being used for window designs, which we will understand in the article ahead.
Why do we need Novel Hydrogel glass windows?
Traditional glass windows are the least energy-efficient building components; hence we need this window system. In the summer, unwanted warmth is caused by near-infrared sunshine passed through windows.
In turn, the strong reflection of the mid-infrared restricts the building’s ability to reject heat. This “greenhouse effect” increases energy usage for cooling. Researchers have proposed this glass system as a countermeasure for this problem. Novel hydrogel-glass design for energy saving in buildings.

Development and innovation of technology and design
A team of researchers from the National University of Singapore (NUS) has developed a novel gel-like polymer that not only effectively dehumidifies ambient air to increase thermal comfort but also harnesses the moisture in the air for a wide range of practical applications, including operating as a sun or privacy screen, conductive ink, and even a battery.
And following water absorption, all of these fascinating qualities are inherent to the material without needing external power.
After this invention’s feat, scientists brought this material’s practical application into reality.
Chinese researchers at Wuhan University have devised a brand-new hydrogel glass design that combines a layer of hydrogel with a layer of regular glass that can selectively block heat from the Sun without blocking its light.
How does Novel hydrogel glass work?
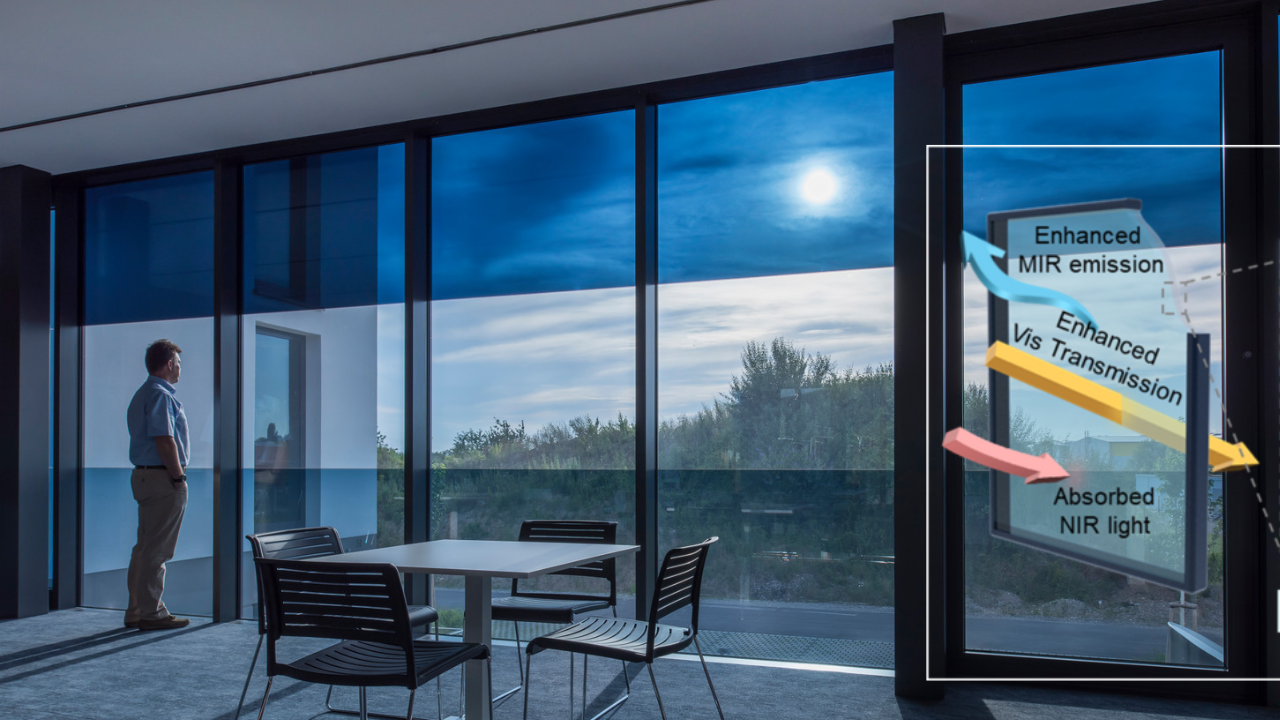
This novel glass comprises two layers: one of hydrogel and the other of regular glass. This indicates that a thin hydrogel coating was applied over the glass in order to reflect more near-infrared light from the environment while enabling more mid-infrared light to pass through from the interior.
In simple words, new hydrogel glass allows a higher level of visible light transmission, stronger near-infrared light blocking, and higher mid-infrared thermal emittance than traditional glass. Contrarily, regular glass is made to let visible light pass through and brighten the space.

The idea is that a photon of visible light, according to the theory, can travel over 1 m (3.3 ft) through water, whereas photons of near-infrared light can barely travel a few millimeters. Hydrogels are primarily composed of water, which makes them a selective barrier.
Since infrared light emits at wavelengths not obstructed by the atmosphere, the team’s testing revealed that the hydrogel glass emitted up to 96% of this light directly into space.
This would maintain a building’s interior temperature lower than other radiative cooling systems. In comparison, ordinary glass emits about 84%. According to New Atlas, after testing on model homes, the researchers found that hydrogel glass might reduce the temperature of a structure by up to 6.3 °F (3.5 °C).
Thanks to all these properties, the researchers demonstrate that hydrogel-glass windows can enhance indoor illumination and reduce the indoor temperature.
Benefits of Hydrogel glasses
- When it comes to eliminating moisture from the air, this innovative hydrogel glass works at least eight times better than other drying agents like silica gel and calcium chloride.
- This hydrogel doesn’t need electricity to function, unlike energy-hungry air-conditioning and dehumidification systems. To carry out the dehumidifying function, it can be simply applied to walls, windows, and even decorative items
- A lot of energy could be saved with new hydrogel glass. It does not require electricity; by design, it is energy efficient and made to conserve energy while making its surroundings cool.
- This material can be used to reduce the relative humidity in indoor and outdoor settings, such as hospital wards, classrooms without air conditioning, parks, and bus stops.
- Hydrogels might also be rolled out rapidly and are inexpensive and simple to obtain, which may offer them an advantage over other, more complicated window solutions.
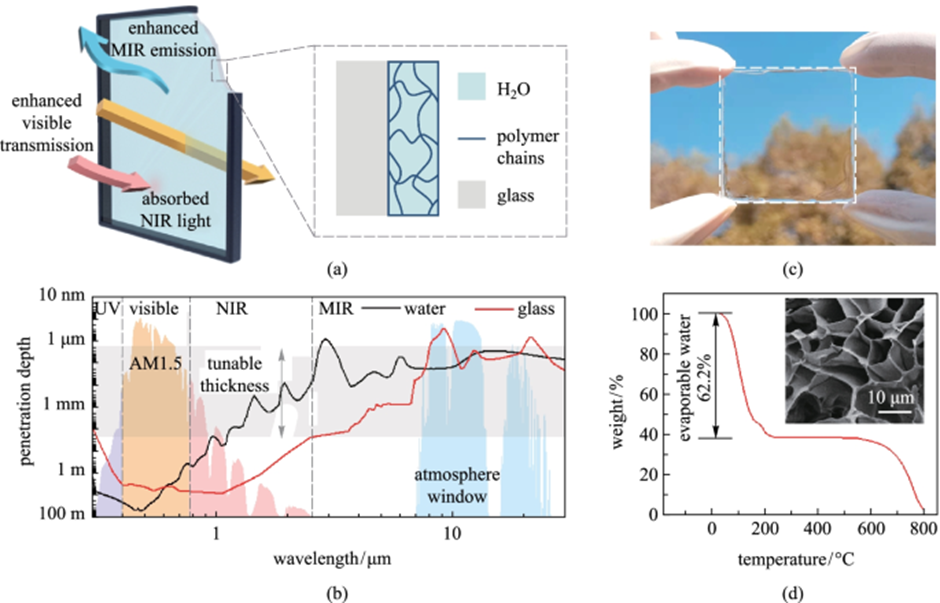
What makes novel hydrogel suitable material for window application?
Apart from its benefits, this material has unique functions and applications.
- The new hydrogel absorbs water from the environment, becomes opaque, and reduces infrared transmission by around 50%. This results in a drop in temperature of the surrounding air of more than seven degrees Celsius. As a result, the hydrogel can be used as a smart window material that also serves as a privacy screen to keep the heat from natural sunshine out. When used with air conditioners, businesses or homes may see energy cost savings since the colder ambient air needs less electricity to chill to the required temperature.
- The research team also found that the hydrogel can produce roughly 1.8 volts of electricity, equivalent to that of an AA battery and enough to power small electronic devices like a digital clock. As a result, the substance can also be used as a backup power source when no sunshine or electricity is available.
- The hydrogel can also be used as conductive ink on printed circuit boards, which are frequently encountered in electronic equipment. The material’s gel-like properties make it a desirable choice for flexible electronics. The hydrogel can be erased easily with common solvents such as vinegar so that the circuit boards can be reused. This would help to cut down on electronic waste.
- We found that, based on simulations, ordinary schools in various places throughout the world may save anywhere from 2.37 to 10.45 MJ/m2 of energy annually. Further, Hydrogel-glass has considerable promise for use in energy-efficient windows due to its broadband light management across the visible and thermal infrared spectrum.
On May 24, 2018, these study results were made available online by the scholarly journal Energy & Environmental Science.
Future prospects and smart window development
NUS and the Ministry of Education of Singapore are providing funding for creating innovative hydrogel.
With assistance from the NUS Industry Liaison Office, the research team has received significant funding from Temasek Foundation Ecosperity to test this novel application on a larger scale in both indoor and outdoor spaces as a result of the promising results of using the hydrogel to reduce relative humidity significantly.
Now, if we talk about the domain of smart window development, a lot has been done. Smart windows have the potential to increase energy efficiency significantly, but as with other recent technological advancements like electric vehicles, there may be some hiccups along the way.
The market value for smart glass is expected to reach $7.5 billion by 2028, thanks to breakthroughs in research over the past few decades that have taken the technology well beyond the lab. Different technologies and concepts are being developed for energy-efficient window systems.
Smart windows’ ability to change between a transparent and a blocking state is made possible by the use of materials that can change their shape in both directions. Some substances change when exposed to heat or electricity ; others respond to a mechanical strain, magnetic field, or humidity level.
There are mainly 2 types of smart windows – Thermochromic and Electrochromic.
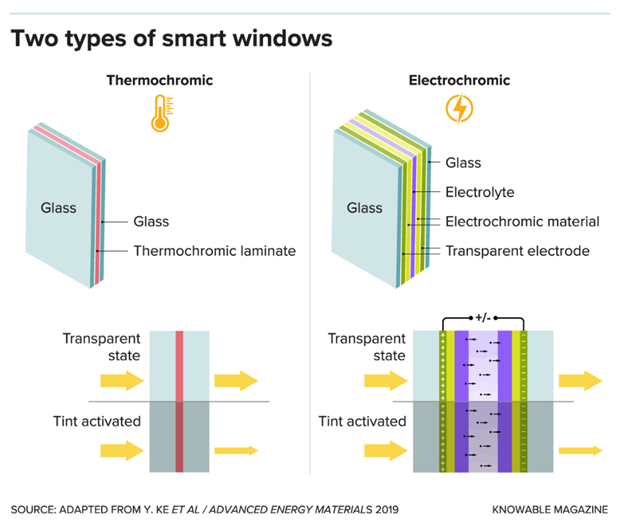
As the technology developed, scientists looked into various materials that can change light in reaction to other stimuli like heat, ultraviolet radiation, and magnetic. Today, a variety of unique “smart materials” are utilized, and researchers are always looking into new ones.
In addition to being present in vehicles like automobiles, boats, and airplanes, smart windows are also beginning to appear in structures like office buildings and airport terminals.
And if they manage to get beyond a few major obstacles, they might one day play a significant part in increasing the energy efficiency of homes. However, the cost must decrease for smart windows to become widely used and reduce everyone’s energy use.
In the future, says materials physicists predict, “there’s no reason really to have any other windows than these smart windows.”
Perfect material for window glasses
According to materials scientist Long Yi of Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, each temperature-responsive material has problems. Each material transitions at different temperatures and can appear more or less colored.
Some materials , like the hydrogel polymer, are excellent at reflecting heat yet have a color that is too opaque to be seen through.
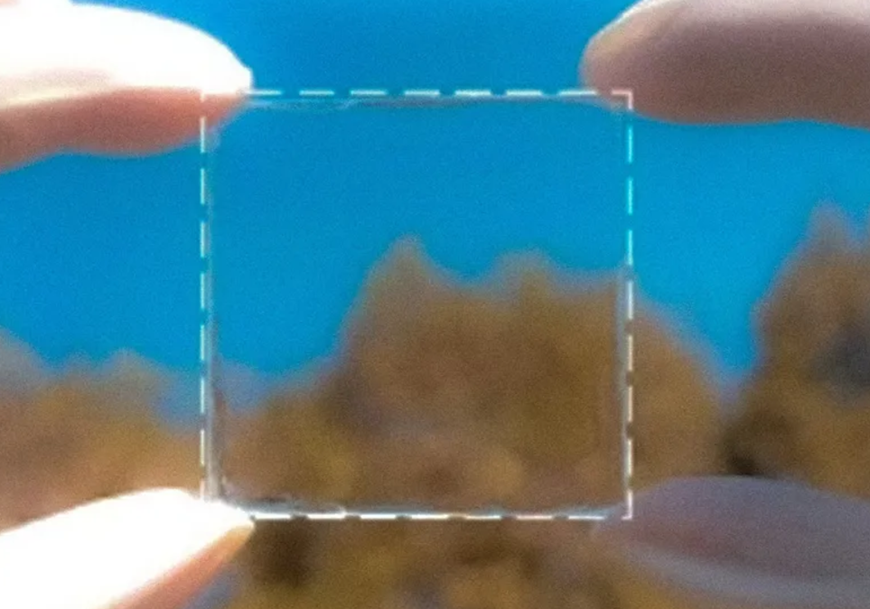
Others, like VO2, are sufficiently transparent to preserve views but are less energy efficient since they are less effective at reflecting heat.
Hence there is no perfect material.
Science keeps developing technology, but at this time, economics mostly determines whether or not smart windows succeed. According to a materials scientist, the cost of smart windows needs to go down for them to become popular.
Conclusion
As we went through a detailed understanding of this rising window design with energy-efficient property, we might deduce that this novel hydrogel glass could keep buildings cooler, hence lowering cooling energy use, which would benefit the environment and people’s wallets.
It helps keep houses and building cool and pleasant. This technology can see various developments in future stages, probably aiming to increase efficiency, reduce energy losses, and be cost-effective.
The expectation is that we will consume less energy and spend less money to keep living rooms cooler without sacrificing outdoor visibility. We should not have to sacrifice comfort for a cleaner and less expensive environment.